COMPUTEX 2025: Arm Charts a Scalable Path for AI from Cloud to Edge
Chris Bergey, Senior Vice President and General Manager of Arm’s Client Line of Business, outlined how Arm and its partners are advancing architectural strategies to support artificial intelligence workloads across every segment of computing—from hyperscale cloud to energy-efficient edge devices.
At COMPUTEX 2025, Arm hosted a landmark executive session titled “From Cloud to Edge: Advancing AI on Arm, Together”, led by Chris Bergey, Senior Vice President and General Manager of Arm’s Client Line of Business. The session outlined how Arm and its partners are advancing architectural strategies to support artificial intelligence workloads across every segment of computing—from hyperscale cloud to energy-efficient edge devices.

Bergey’s central message: AI is no longer a speculative future—it is a present-day computing reality. The industry is at a critical inflection point where foundational infrastructure choices will determine long-term competitiveness.
AI as a Generational Shift in Technology
Opening the session, Bergey emphasized that this is not simply another product cycle or iteration of past innovations. The rise of AI represents a transformation more significant than the internet or smartphones, fundamentally changing how technology is built, deployed, and experienced.
In the past 18 months alone, more than 150 new foundational models have been introduced, many of which exceed 90% accuracy. The industry has rapidly transitioned to multimodal models, and real-world use cases—from coding assistants to customer support agents—are generating hundreds of millions in revenue with minimal teams and infrastructure.
Edge AI Maturity: From Concept to Commercialization
A key highlight of the session was the shift from cloud-centric AI to edge-native intelligence. While AI assistants once required cloud infrastructure, Arm-powered on-device AI is now enabling new classes of intelligent systems, such as:
- Smart eyewear (e.g., Ray-Ban Meta smart glasses)
- AI PCs with fanless designs and extended battery life
- Autonomous vehicles and industrial systems
This evolution is unlocking experiences that were previously impossible due to latency, connectivity, or power constraints. Arm’s architecture enables energy-efficient, high-performance AI processing in constrained form factors.
Arm’s Position in the Cloud: Efficiency at Hyperscale
Arm’s cloud strategy is rapidly gaining momentum. Bergey highlighted Arm’s strong presence in the hyperscaler ecosystem:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): Over 50% of AWS's new CPU deployments over the past two years are based on Graviton processors, built on Arm architecture. Moreover, 90% of the top 1000 EC2 customers are now using Graviton-based instances.
- Other Cloud Providers: Microsoft (Cobalt), Google (Axion), Oracle (Ampere partnership), and Alibaba (Yitian) have all introduced custom Arm-based infrastructure.

These platforms benefit from up to 40% better power efficiency, a critical factor as AI-first data centers push toward gigawatt-scale energy usage. In Taiwan alone, a projected 8x increase in data center power consumption underscores the urgency of efficient computing.
AI Workloads Demand New Architectures
Traditional server architectures—designed for basic compute and web hosting—are becoming increasingly inadequate for modern AI. Bottlenecks in CPU throughput and I/O density hinder the scalability of AI training and inference pipelines.

To address this, industry leaders like NVIDIA have pivoted to co-designed AI infrastructure, pairing GPUs with tightly integrated Arm-based CPUs. This includes platforms such as:
- Grace Hopper and Grace Blackwell superchips
- Vera Rubin AI cluster, leveraging Arm-based CPUs for balance and throughput
Arm enables this shift through scalable, power-efficient processor designs tailored for AI, whether deployed in AI “factories” or compact edge environments.
Kleidi: Arm’s Optimized AI Software Stack
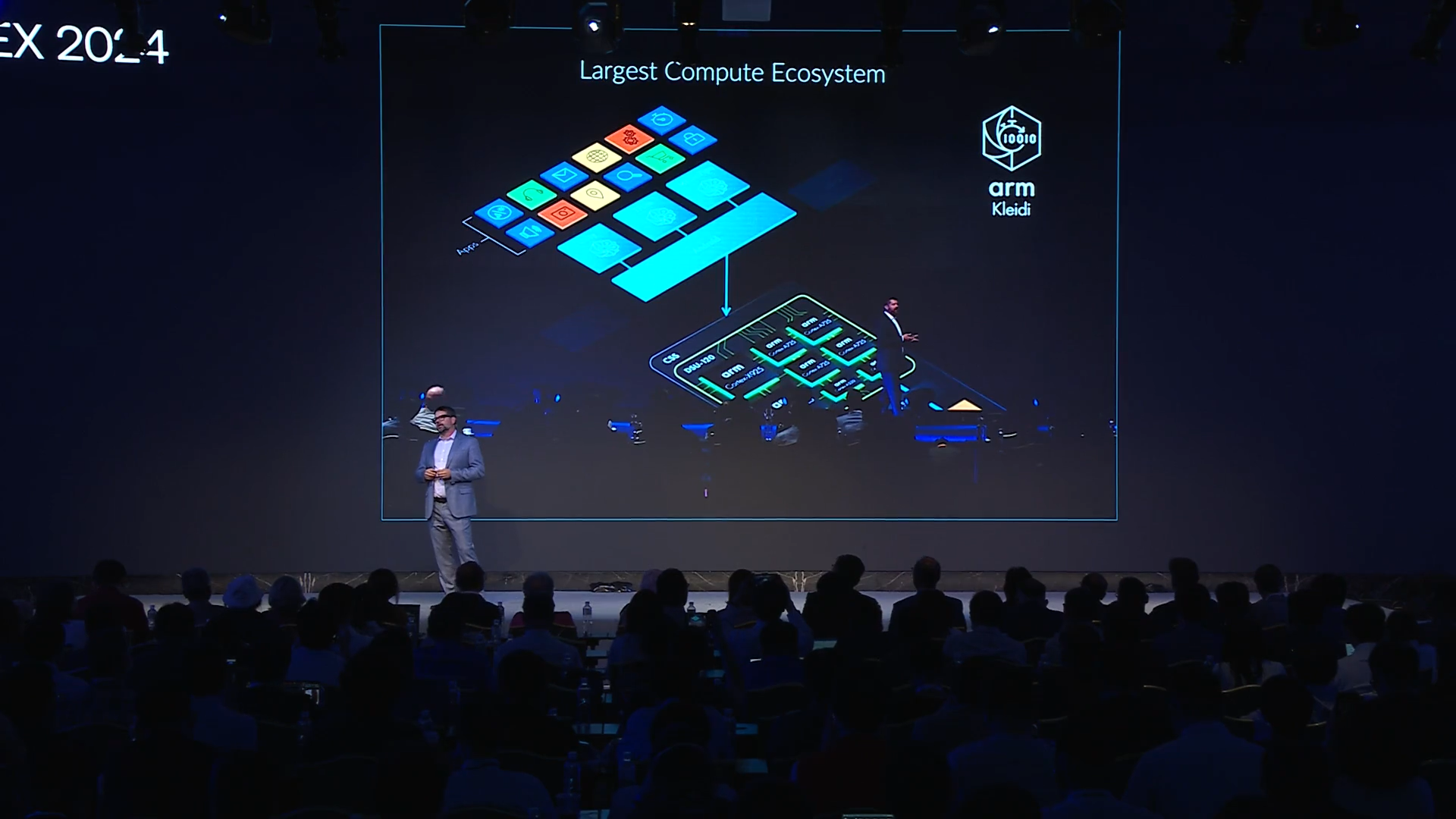

A cornerstone of Arm’s AI enablement strategy is its investment in software. In 2023, Arm introduced Kleidi, a collection of libraries that optimize AI workloads on Arm-based CPUs by extending support for common open-source AI frameworks.
As of 2025, Kleidi is integrated with:
- ONNX Runtime (Microsoft)
- TensorFlow Lite RT (Google)
- Meta’s ExecuTorch
- Tencent’s Hunyuan framework

This ensures that developers can leverage Arm’s v9 architecture, including Scalable Matrix Extensions (SME), to accelerate inference tasks without requiring custom low-level optimization.
With over 8 billion software library installations, Arm is solidifying its position as both a hardware and software platform vendor for AI.
Performance per Watt: The Non-Negotiable Metric
Throughout the session, Bergey reiterated Arm’s enduring focus on performance per watt, calling it the most critical metric in AI infrastructure.

In environments ranging from smartphones to cloud data centers, energy constraints are now a primary design consideration. As workloads become more compute-intensive, Arm’s architectural advantage in efficiency becomes more strategic.
This is particularly vital for AI inference, where the volume of usage dwarfs the initial cost of training. Bergey cited that:
- Training a model may require 10²⁶ FLOPS
- Running a single inference may require 10¹⁵ FLOPS
- But the total inference compute load globally exceeds training demands by multiple orders of magnitude
Enabling the AI PC: Arm’s Client-Side Innovation

Arm also detailed advancements in its Client Compute Solutions (CSS). The next generation includes:
- “Travis” CPU: A new high-performance core with double-digit IPC gains and built-in support for SME, enabling efficient on-device AI.
- “Krake” GPU (previously referenced in press as “Draga”): Designed for console-class gaming, extended ray tracing, and sustained AI graphics performance.
These platforms are already being adopted across Windows on Arm, Chromebooks, and Android devices, with OEMs like MediaTek leveraging them to deliver high-efficiency AI subsystems.
According to Bergey, over 40% of PCs and tablets shipped in 2025 are expected to be Arm-based, reflecting growing market alignment around AI-capable, low-power platforms.
Taiwan’s Strategic Role in AI Infrastructure

Bergey concluded by emphasizing Taiwan’s pivotal role in the global AI supply chain. From SoC design and semiconductor packaging to OEM manufacturing, Taiwan is not just participating in AI’s future—it is foundational to it.
Arm views collaboration as essential to realizing AI’s full potential. By working with global partners on silicon design, system integration, and software enablement, Arm aims to accelerate time-to-market for AI products that scale—from hyperscale infrastructure to edge devices.
Conclusion: Strategic Takeaways for CTOs
The session delivered a clear and actionable thesis: AI is a systemic transformation, not a feature update. Organizations must rethink compute strategy holistically—integrating AI enablement into every layer of the stack.
Arm’s role as a cross-domain platform—from hyperscaler CPUs to mobile chipsets—provides an end-to-end foundation for building, deploying, and scaling AI systems efficiently. For CTOs, the imperative is to adopt architectures that support the power, performance, and developer needs of a rapidly evolving AI landscape.
The future of AI will be heterogeneous, distributed, and developer-led—and according to Arm, those who build with platform-first thinking today will define tomorrow’s innovation frontier.


